In the ever-evolving world of IT and software development, ensuring system reliability, performance, and scalability is more critical than ever. That’s where SRE, or Site Reliability Engineering, comes into play. This discipline bridges the gap between development and operations by applying software engineering principles to infrastructure and operations problems.
In this article, we’ll uncover the full form of the SRE process, explain its core components, and explore why it’s vital for modern IT organizations.
What is SRE? (Full Form & Definition)
SRE stands for Site Reliability Engineering. It is a set of principles and practices that incorporates software engineering approaches to solve IT operations problems. Originally pioneered by Google, SRE helps organizations build and maintain highly reliable and scalable systems.
In simpler terms, SRE ensures that websites, applications, and services remain up and running efficiently, even as they scale to support millions of users.
Core Components of the SRE Process
The SRE process is not a one-time activity; it’s a continuous lifecycle that focuses on balancing system reliability with feature velocity. Below are the key pillars that make up the SRE process:
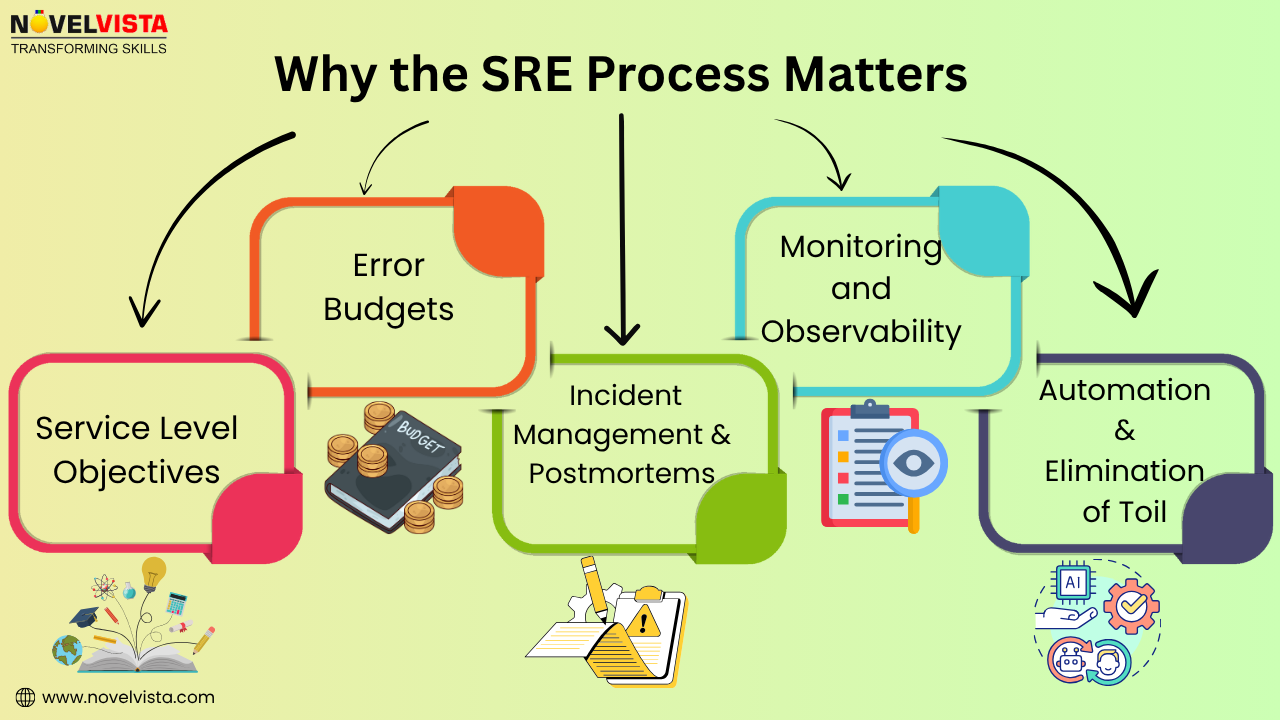
1. Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Indicators (SLIs)
SLIs are metrics that measure aspects like latency, availability, and error rates.
SLOs are targets for these indicators, providing a threshold for acceptable performance.
Together, they help define what reliability looks like for a given system.
2. Error Budgets
The difference between 100% availability and your SLO target (e.g., 99.9%) is the error budget.
It allows developers to take risks and innovate without compromising reliability.
3. Incident Management & Postmortems
SRE teams handle incident response, including detection, mitigation, and communication.
After resolving an issue, a blameless postmortem is conducted to understand root causes and improve systems.
4. Monitoring and Observability
Real-time monitoring tools and logs help detect anomalies.
Observability enables understanding why a system is behaving a certain way, not just that it’s behaving differently.
5. Automation & Elimination of Toil
SRE emphasizes automating repetitive tasks and manual operations to reduce human error and increase efficiency.
This “toil reduction” helps engineers focus on engineering solutions rather than firefighting.
Why the SRE Process Matters
✅ Improved System Reliability
SRE ensures systems stay up and available. Downtime costs businesses money and trust—SRE helps minimize both.
✅ Faster Product Releases
With a structured balance between reliability and speed (via error budgets), SRE enables faster deployment without sacrificing quality.
✅ Better Incident Response
SRE teams are prepared for outages. Their incident handling playbooks and tools allow them to restore services quickly.
✅ Enhanced Collaboration
SRE promotes DevOps culture by encouraging collaboration between developers and operations, resulting in more reliable software delivery.
✅ Customer Satisfaction
End-users experience fewer bugs, less downtime, and better performance, leading to increased trust and retention.
Who Should Implement SRE?
Tech Startups aiming for scale
Large Enterprises managing distributed systems
E-commerce Platforms, Fintech Apps, Cloud Service Providers, and others, where uptime and performance are critical
If your business relies on digital services, adopting the SRE process can be a game-changer.
Ready to start your SRE journey?
Join the growing community of Site Reliability Engineers with NovelVista’s SRE Foundation Certification and gain the skills to power next-generation IT systems.
Final Thoughts
Site Reliability Engineering isn’t just a trend—it’s a proven approach to building and managing resilient systems. By uncovering the SRE process and understanding its components, organizations can deliver robust, scalable, and efficient digital services.
Whether you're an IT leader, engineer, or business stakeholder, integrating the SRE mindset into your operations is essential for long-term success in the digital age.



















Write a comment ...